|
The main
objective of this work was to determine whether the IDDSI thickness levels are
sufficiently differentiated to be treated as valid therapeutic thickness levels
for the treatment of dysphagia of differing severity as assessed using a
validated water protocol, by establishing a correlation between IDDSI thickness
levels and dysphagia grades of Water Drinking Test.
Ms.
Mingsong Su and Gangying Zheng have been focusing on
the study of the classification of liquids and semi-solids which frequently
lead to aspiration and cough for dysphagia. The work was conducted in
collaboration with Prof. Jianqin Sun and her group at Huadong Hospital in
Shanghai. Ourdiet Swallow (Ourdiet, Guangzhou, China), a commercial thickener
product, was used for the test. Four liquid samples of different concentrations
(0.54, 1.16, 2.36, and 4.20 %) were found at the boundaries of each of levels
0, 1, 2, and 3 according to Flow Test provided by IDDSI. The shear viscosity
was measured using a DHR-2 rheometer (TA Instruments, New Castle, USA) with a
cone-and-plate geometry (diameter = 40 mm, angle = 2.008°). Apparent shear
viscosity of sample 0.54, 1.16, 2.36, and 4.20% at 50 s-1 were determined to be
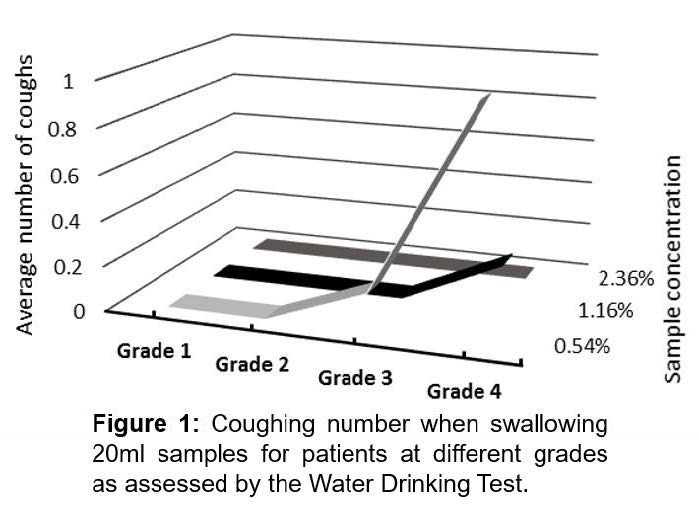
37.2, 84.1, 206.4, and 434.6 mPa•s, respectively. Altogether 26 elderly
subjects were recruited and assessed for their dysphagia grades using the Water
Drinking Test. Subjects were provided with a series of samples based on a
modified Volume-Viscosity Swallow Test (V-VST) test and the swallowing
performance (time of swallowing, number of swallows, and number of coughs) was
recorded and analyzed (Fig.1).
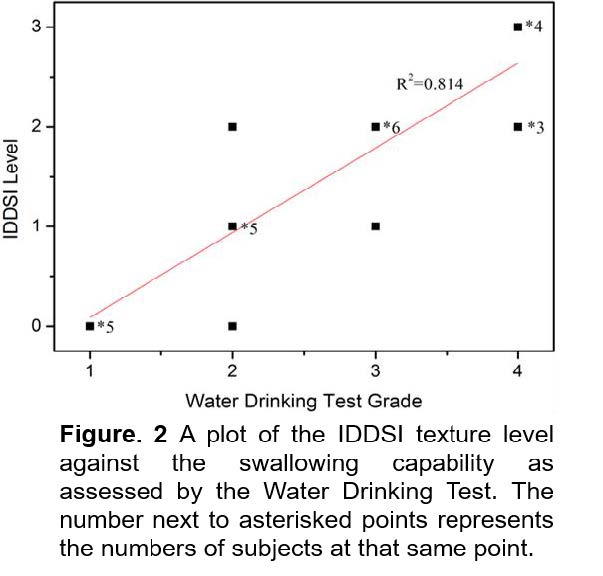
Strong
correlations among swallowing capability parameters were observed. More
importantly, results from this work clearly demonstrated that severity of
dysphagia with water-based swallows correlates positively with IDDSI thick-ness
levels aimed at reducing dysphagia symptoms in those patients (Fig.2),
confirming the reliability and feasibility of IDDSI framework for clinical
applications. This work is accepted for publication in Journal of Texture
Studies.
|
